Not all sewing machines are equipped with servo motors, marking a distinction in the realm of sewing technology.
While servo motors have gained prominence for their advanced features, offering variable speed control, quiet operation, and energy efficiency, many traditional and simpler sewing machines still utilize different motor types.
Factors such as cost considerations, the simplicity of operation, and the specific applications of certain machines contribute to the diversity in motor choices.
Understanding whether a sewing machine features a servo motor involves considering its design, purpose, and technological specifications.
This diversity allows users to choose machines tailored to their specific needs and preferences in the dynamic landscape of sewing technology.
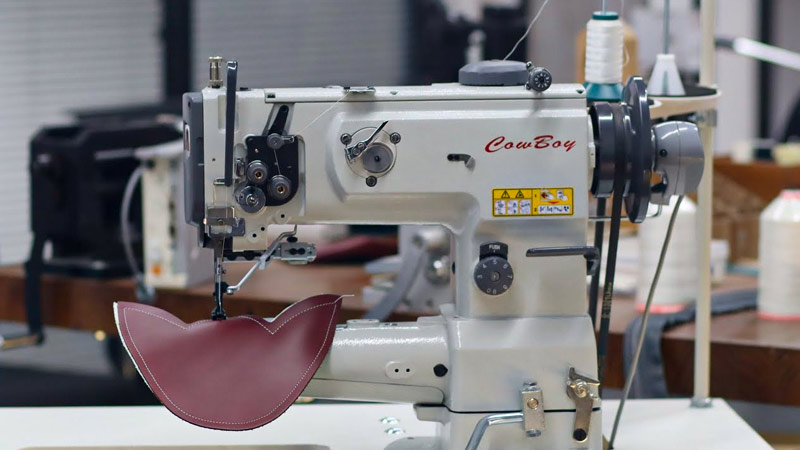

What Is a Servo Motor in a Sewing Machine?
A servo motor in a sewing machine is an advanced, electronically controlled motor that provides precise speed control and instant start-stop functionality.
Unlike traditional motors, servo motors offer variable speed adjustments, ensuring accuracy in stitching and operating quietly.
Known for energy efficiency, they consume power only during use. The compact design and low heat generation suit various sewing machine models.
Compatible with computerized systems, servo motors enable automation and synchronization with digital controls.
Their inclusion enhances performance, safety, and user experience, making them a preferred choice, especially in industrial and high-precision domestic sewing applications.
Do All Sewing Machines Have Servo Motors?
No, not all sewing machines have a servo motor. There are various types of sewing machines, and they can be categorized based on their motors.
While servo motors are commonly found in modern sewing machines, especially in industrial and advanced domestic models, many machines still use different types of motors.
Here are some reasons why not all sewing machines have servo motors:
Traditional Machines
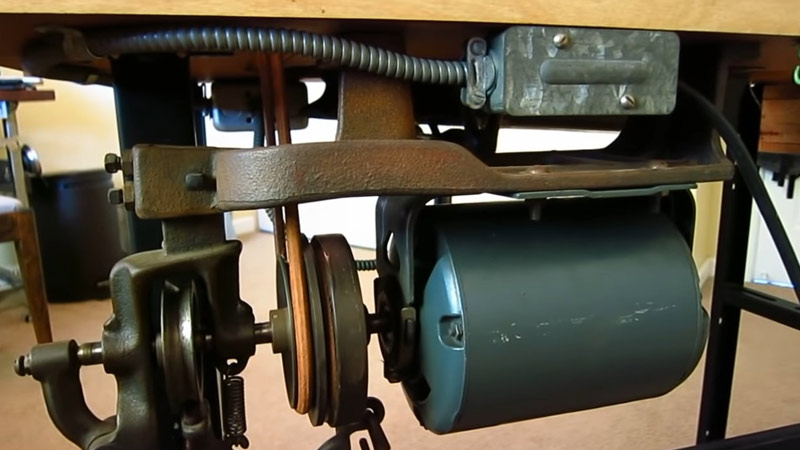

Many older sewing machines, particularly those manufactured before the widespread adoption of servo motors, are equipped with traditional motors.
These motors, such as clutch motors, operate on a different mechanism. Clutch motors are known for their straightforward on/off functionality, providing a constant speed when engaged.
While lacking the variable speed control of servo motors, they are sufficient for basic sewing tasks and are often found in vintage or entry-level machines.
Cost Considerations
Servo motors can be more expensive to manufacture and install than traditional motors.
In an effort to produce affordable sewing machines, manufacturers may opt for cost-effective motor options.
This is especially true for machines designed for beginners or those on a budget, where keeping the overall cost low takes precedence over advanced motor features.
Simplicity of Operation
Some users may prefer the simplicity of machines with basic motors that have straightforward on/off controls.
Especially for those who perform repetitive tasks at a constant speed, the additional features provided by a servo motor may be unnecessary. A simpler motor may suffice without needing variable speed control for these users.
Specific Applications
Specialized sewing machines, designed for specific materials or tasks, may use motors tailored to their unique requirements.
For example, heavy-duty sewing machines used for leather or upholstery work might prioritize torque and power over the variable speed control servo motors offer.
In such cases, the chosen motor aligns with the specific demands of the machine’s intended applications.
Repair and Maintenance Considerations
Traditional motors, especially clutch motors, are renowned for their durability and ease of maintenance.
Repairing or maintaining these motors is often simpler and requires less specialized knowledge than more modern servo motors.
In certain environments, such as industrial settings, where reliability is crucial, the robustness and familiarity of traditional motors may outweigh the benefits of upgrading to a servo motor.
What Are the Advantages of Servo Motors in Sewing Machines?
Servo motors have become increasingly popular in modern sewing machines due to their advanced features that enhance precision, control, and energy efficiency.
Here are some key advantages of servo motors in sewing machines:
Variable Speed Control

One of the primary advantages of servo motors is their ability to provide precise variable speed control.
This feature allows sewers to adjust the stitching speed according to the complexity of the task, fabric type, or their personal preference.
Variable speed control is especially beneficial when working on intricate details or delicate materials.
Quiet Operation
Servo motors are known for their quiet and smooth operation. Unlike the traditional clutch motors that can be noisy when running, servo motors operate quietly, creating a more comfortable and less disruptive sewing environment.
This is particularly advantageous in both home and industrial settings where noise reduction is a consideration.
Energy Efficiency
Servo motors are more energy-efficient compared to traditional motors. They consume power only when in use, unlike clutch motors that run continuously even when the machine is idle.
This energy-saving feature reduces electricity costs and contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly sewing operation.
Instant Start and Stop
Servo motors offer instant start and stop functionality. This rapid response allows for greater control over the sewing process, facilitating precise stitching and making it easier to handle intricate patterns or sudden changes in sewing direction.
The immediate stop also enhances safety by minimizing the risk of overshooting stitches.
Built-in Brake System
Many servo motors come equipped with a built-in brake system. This feature ensures that the sewing machine stops promptly when the foot pedal is released, preventing the needle from continuing unnecessary movements. The brake system adds extra control and safety to the sewing process.
Compact and Lightweight Design
Servo motors are generally more compact and lightweight than traditional motors. This makes them suitable for various sewing machine models, including portable and tabletop machines.
The reduced size contributes to the overall portability and maneuverability of the sewing machine.
Low Heat Generation
Servo motors generate less heat during operation compared to traditional motors. This contributes to the motor’s longevity and ensures that the sewing machine remains cooler, especially during prolonged use.
Reduced heat production is beneficial for preventing overheating and maintaining optimal working conditions.
Compatibility with Computerized Systems
Servo motors seamlessly integrate with computerized sewing machine systems. This compatibility allows for more advanced automation, programmability, and synchronization with digital controls.
Sewing machines with servo motors can be part of sophisticated production lines and are suitable for intricate embroidery or quilting patterns programmed through computer interfaces.
Are All Sewing Machines Compatible With Servo Motors?

No, not all sewing machines are inherently compatible with servo motors. The compatibility of a sewing machine with a servo motor depends on the machine’s design, build, and intended use.
Here are some factors that determine whether a sewing machine can be equipped with a servo motor:
Mechanical Design
Older or simpler sewing machines, especially those designed with traditional motors like clutch motors, may not be structurally compatible with servo motors.
Integrating a servo motor often requires redesigning the machine’s internal components, mounting brackets, and pulley systems.
Size and Form Factor
Servo motors come in various sizes, and not all sewing machines have the necessary space or structure to accommodate them.
Some smaller or more compact machines may lack the physical space required to install a servo motor.
Manufacturers design servo motors in different sizes to cater to various sewing machine models, but customization might sometimes be necessary.
Purpose and Application
While servo motors are versatile and suitable for various sewing applications, certain specialized sewing machines may have unique motor requirements.
For example, heavy-duty industrial machines designed for specific tasks, such as leather or upholstery work, might have motors tailored to handle the demands of those applications.
Manufacturers’ Specifications
Manufacturers design sewing machines with specific motors in mind. While some sewing machines are initially designed to be compatible with servo motors, others may require additional adjustments or adaptations.
Checking the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines is crucial to determine whether a particular sewing machine model is compatible with a servo motor.
Electronic Control System
Servo motors are designed to work seamlessly with electronic control systems, providing precise speed adjustments.
Older mechanical sewing machines without electronic control systems may not be compatible with servo motors without additional modifications.
The integration of a servo motor may require the addition of electronic components to facilitate communication between the motor and the sewing machine.
Cost Considerations
While servo motors offer advanced features, some entry-level or budget-friendly sewing machines may not be designed to be compatible with servo motors due to cost considerations.
Manufacturers may prioritize affordability over including advanced motor technology in certain models.
Aftermarket Modifications
In some cases, even if a sewing machine was not originally designed for a servo motor, aftermarket modification kits may be available.
These kits often include the necessary components and instructions to retrofit a sewing machine with a servo motor.
However, the success of such modifications may vary depending on the specific machine model and the availability of compatible kits.
FAQs
Are all sewing machines equipped with servo motors?
No, not all sewing machines come with servo motors. The inclusion of servo motors varies based on the machine’s design, intended use, and technological specifications.
What are the advantages of sewing machines with servo motors?
Sewing machines with servo motors offer benefits such as variable speed control, quiet operation, energy efficiency, and instant start-stop functionality. These features contribute to enhanced precision and user control.
Do traditional sewing machines use servo motors?
Traditional sewing machines, especially older models, may not use servo motors. They often rely on different motor types like clutch motors or belt-driven systems.
Can I retrofit my sewing machine with a servo motor?
In some cases, yes. Aftermarket modification kits may be available to retrofit certain sewing machines with servo motors, but success depends on the machine model and compatibility.
Why might a sewing machine not have a servo motor?
Sewing machines may lack servo motors due to factors such as cost considerations, simplicity of operation, specific applications, or the absence of electronic control systems in certain models.
To Recap
The presence of servo motors in sewing machines is not universal, showcasing the diverse landscape of sewing technology.
While servo motors offer advanced features like variable speed control and energy efficiency, traditional machines with different motor types continue to play a significant role.
Factors such as cost, simplicity, and specific applications influence the choice of motors in sewing machines.
This diversity accommodates various user preferences, ranging from those seeking cutting-edge technology for intricate tasks to users who value simplicity and cost-effectiveness.
Whether equipped with servo motors or not, sewing machines cater to a wide spectrum of needs, highlighting the adaptability and versatility of this essential tool in the realm of fabric arts.
Leave a Reply