“Hmong Embroidery,” known as “paj ntaub” in the Hmong language, is a captivating and culturally rich art form that transcends mere stitches and threads.
Translating to “flower cloth,” this traditional embroidery is deeply rooted in the history of the Hmong people, originating from their ancient roots in southern China.
“Paj ntaub” is not just a craft; it is a visual language that intricately weaves stories, beliefs, and identity into vibrant and symbolic designs. Each stitch in Hmong embroidery tells a tale of resilience, cultural preservation, and the enduring spirit of a community.
This introduction sets the stage for an exploration of the art’s historical, cultural, and artistic dimensions.
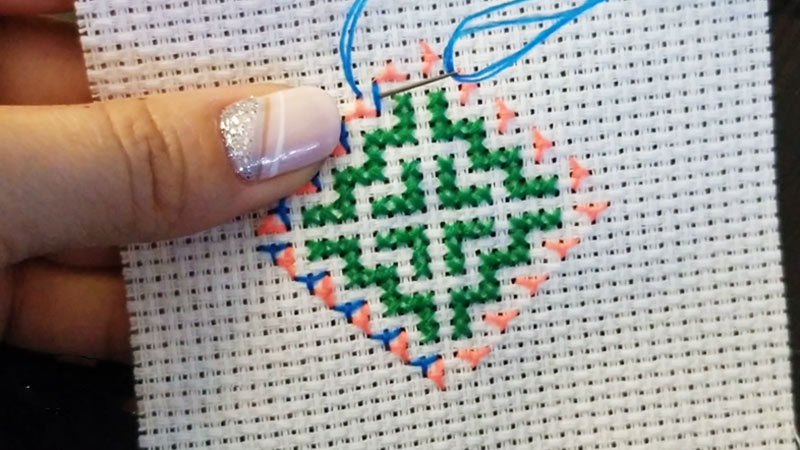

What Is Hmong Embroidery Called?
Hmong embroidery is referred to as “paj ntaub” in the Hmong language. Translating to “flower cloth” in English, this traditional embroidery is an integral part of Hmong cultural expression.
“Paj ntaub” features intricate floral motifs and serves as a visual language, depicting the rich history, beliefs, and daily life of the Hmong people. Beyond its aesthetic appeal, this art form is a means of storytelling and cultural preservation.
The detailed craftsmanship and symbolic significance embedded in each stitch make “paj ntaub” a vibrant and meaningful representation of Hmong heritage and identity.
History of Hmong Embroidery
The history of Hmong embroidery is a captivating narrative that intertwines cultural preservation, artistic expression, and the resilience of the Hmong people.
Let’s explore the historical journey of Hmong embroidery through different phases.
Ancient Roots in China
Hmong embroidery has ancient origins in southern China, evolving from traditional textile practices and influenced by the ancient Hmong script. It has been an integral part of the Hmong culture for thousands of years.
Migration Patterns
The Hmong people’s history involves migration from southern China to Southeast Asia, impacting the evolution of their embroidery techniques. Adaptations to diverse cultures and environments during this journey enriched the art form.
Cultural Preservation
Hmong embroidery emerged as a powerful tool for cultural preservation, serving as a visual language to express identity and clan affiliations and document the history of the Hmong people. It became a means of storytelling and cultural transmission.
Symbolism and Storytelling
Motifs in Hmong embroidery, such as flowers and animals, hold deep symbolic meanings. Story cloths, a unique form of embroidery, became a visual narrative, allowing Hmong women to tell stories, depict daily life, and convey cultural beliefs.
Adaptation and Evolution
Hmong embroidery adapted to changing circumstances over time. Migration, exposure to new cultures, and the use of different materials influenced the art form, ensuring its continued relevance while preserving its core identity.
Contemporary Significance
In modern times, Hmong embroidery has expanded beyond traditional garments. It is utilized in fashion, home decor, and collaborations with contemporary designers. Hmong women continue to play a crucial role in preserving and evolving this cultural tradition.
What Are the Symbolic Meanings Behind Hmong Embroidery Motifs?
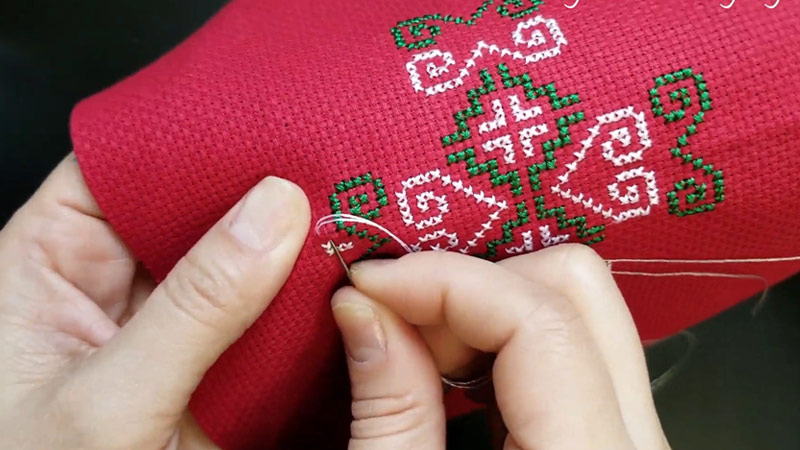

Hmong embroidery motifs carry deep symbolic meanings, reflecting the cultural, spiritual, and historical aspects of the Hmong people.
Here are some examples of symbolic meanings behind Hmong embroidery motifs:
Flowers
Flowers often represent the natural environment and the harmony between humans and nature in Hmong culture. Different types of flowers may carry specific meanings, such as prosperity, beauty, and connection to the land.
Animals
Animals depicted in Hmong embroidery often hold symbolic significance. For instance, the elephant’s foot motif symbolizes strength and protection, while the snail motif represents patience and perseverance.
Animals can convey virtues, cultural beliefs, and connections to ancestral stories.
Geometric Shapes
Geometric shapes in Hmong embroidery can represent various aspects of life and culture. For example, triangles may symbolize mountains, squares can represent homes or stability, and diamonds may symbolize femininity.
Paj Ntaub (Flower Cloth) Patterns
The overall design of Hmong embroidery, known as “paj ntaub” or flower cloth, signifies the interconnectedness of life. The repetitive patterns reflect the cyclical nature of existence and the interdependence between humans and nature.
Story Cloths
Story cloths, a unique form of Hmong embroidery, serve as visual narratives of personal and collective experiences. Each stitch tells a story, documenting the Hmong people’s history, struggles, and triumphs.
Story clothes are a powerful means of cultural preservation and storytelling.
Colors
Colors play a crucial role in Hmong embroidery, each carrying specific meanings. For example, white symbolizes purity, black represents endurance, and green signifies harmony with nature. The combination of colors in a piece can convey a complex narrative and emotional depth.
Types of Hmong Embroidery Techniques
Hmong embroidery boasts a rich array of techniques that contribute to its intricate and culturally significant designs.
Here are the different types of Hmong embroidery techniques:
Cross-Stitch
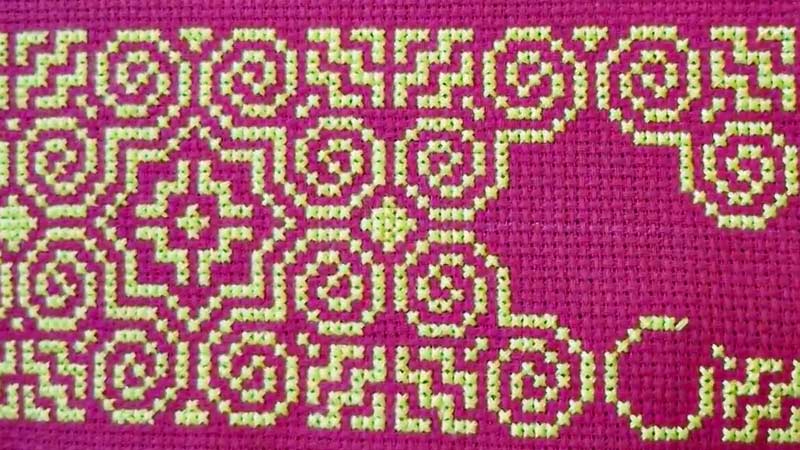

Cross-stitch is a foundational technique in Hmong embroidery, involving the creation of X-shaped stitches on fabric. This method is widely used to produce symmetrical and detailed patterns, often featuring geometric shapes, flowers, and animals.
Appliqué
Appliqué is a technique where cut-out fabric shapes are attached to a base fabric using stitches. Hmong artisans use this method to incorporate vibrant colors into their designs, creating visually striking motifs such as flowers and animals.
Reverse Appliqué
Unique to Hmong embroidery, reverse appliqué involves cutting away layers of fabric to reveal contrasting colors underneath. This technique adds depth and complexity to the designs, resulting in visually captivating and layered patterns.
Batik
Batik is a dyeing technique where hot wax is applied to fabric before dyeing, creating patterns as the wax acts as a resist. In Hmong embroidery, batik adds vibrant colors and intricate detailing to the fabric, contributing to bold and textured designs.
Counted Thread
Counted thread embroidery in Hmong textiles involves carefully counting fabric threads to create precise patterns. This technique is known for its meticulous geometric designs and fine detailing, showcasing the skill and precision of Hmong embroiderers.
How Is Hmong Embroidery Used in Modern Times?

Hmong embroidery has seamlessly transitioned into modern times, finding diverse applications beyond traditional clothing.
Here are ways in which Hmong embroidery is used in contemporary settings:
Fashion and Accessories
Hmong embroidery is incorporated into modern fashion, with traditional designs adorning clothing items such as dresses, blouses, and jackets.
Additionally, accessories like bags, scarves, and hats showcase the intricate beauty of Hmong embroidery, blending tradition with contemporary style.
Home Decor
Hmong embroidery is featured in various home decor items, including pillows, wall hangings, and table runners. These pieces bring a touch of cultural richness and vibrant artistry to modern interiors, allowing individuals to incorporate Hmong heritage into their homes.
Quilts and Bedding
Modern quilts and bedding often feature Hmong embroidery, with stitched patterns adding a unique and personalized touch to bedrooms. These items not only serve a practical purpose but also contribute to the preservation of Hmong cultural heritage.
Art and Craft Products
Hmong embroidery is employed in creating a wide range of art and craft products. From framed embroidered artworks to handcrafted ornaments, Hmong artisans showcase their creativity, turning traditional techniques into contemporary art pieces.
Cultural Preservation and Education
Organizations and individuals use Hmong embroidery to educate others about the culture and history of the Hmong people.
Workshops, exhibitions, and cultural events often feature Hmong embroidery as a means of preserving and sharing this traditional art form with a broader audience.
Commemorative Items
Hmong embroidery is used to create commemorative items for special occasions such as weddings, birthdays, and festivals. These items serve as cherished keepsakes, blending cultural significance with personal celebrations.
Collaborations and Contemporary Design
Hmong embroidery has been incorporated into collaborations with contemporary designers, showcasing its adaptability and relevance. Collaborations often result in unique and innovative products that bridge traditional craftsmanship with modern aesthetics.
FAQs
What does “paj ntaub” mean?
“Paj ntaub” is a Hmong term meaning “flower cloth,” representing the intricate and symbolic floral motifs in Hmong Embroidery.
Are there regional variations in Hmong Embroidery styles?
Yes, regional variations exist, influenced by the diverse environments encountered during Hmong migrations. Different regions may showcase unique embroidery techniques, colors, and motifs.
How do Hmong women pass down the art of embroidery through generations?
The art of Hmong Embroidery is traditionally passed down from older generations to younger women within families. This intergenerational transmission ensures the preservation of techniques, motifs, and cultural significance.
Can Hmong Embroidery be customized for special occasions?
Yes, Hmong Embroidery is often customized for special occasions like weddings and festivals. These personalized creations serve as unique, culturally rich items for celebratory events.
To Recap
“Hmong Embroidery,” known as “paj ntaub,” is a testament to the enduring legacy and creativity of the Hmong people.
Through intricate stitches and vibrant designs, this traditional art form preserves the cultural identity, history, and beliefs of the Hmong community.
The term “paj ntaub,” meaning “flower cloth,” encapsulates the beauty and symbolism woven into every creation. As we unravel the threads of Hmong embroidery, we discover not just a craft but a profound visual language that transcends time.
This art form, with its roots in ancient traditions, continues to bloom, connecting generations and sharing the rich tapestry of Hmong heritage with the world.
Leave a Reply