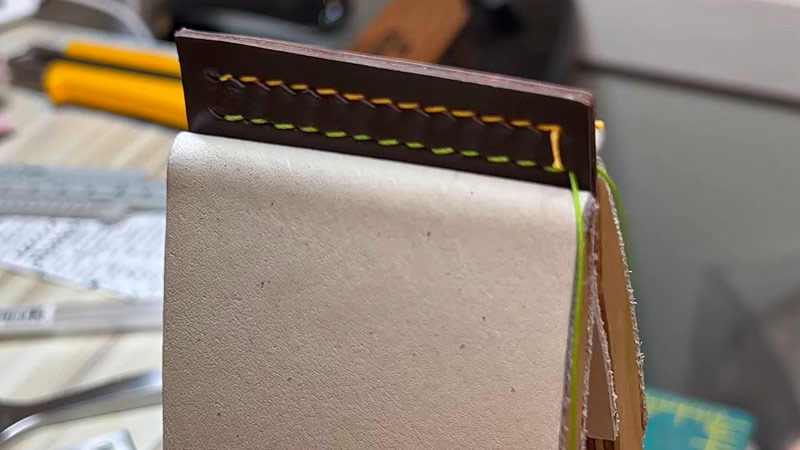
Saddle stitch is a classic and versatile sewing technique that finds its roots in traditional craftsmanship.
It involves using a single continuous thread and a needle to create a series of interlocking loops, resulting in a sturdy and visually distinctive seam.
Widely employed in bookbinding and leatherworking, saddle stitch offers a handcrafted touch and is renowned for its durability. Unlike machine stitching, this method requires skill, precision, and a keen eye for detail.
Its visible knots or loops contribute to its unique aesthetic, making it a favored choice for those seeking a more artisanal and personalized finish in their sewing projects.
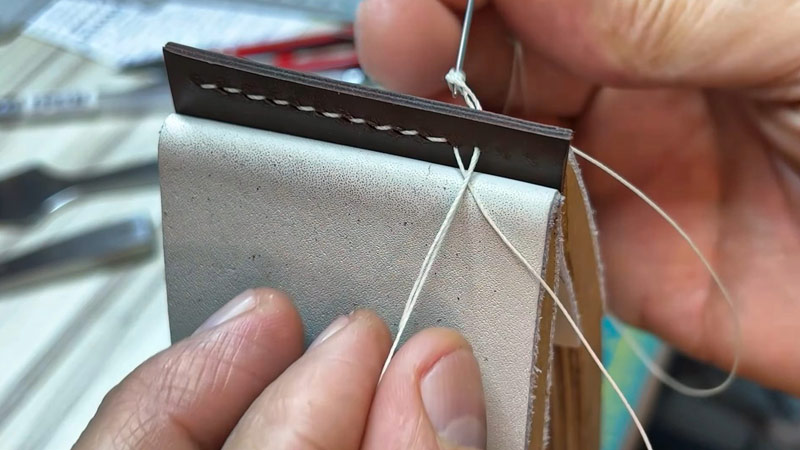

What Is Saddle Stitch in Sewing?
Saddle stitch is a traditional and time-honored method of sewing, primarily used in bookbinding and leatherworking.
This technique involves sewing together folded sheets of paper or leather by passing a threaded needle through the center of the fold, creating a secure and durable binding.
Saddle stitching is known for its simplicity, strength, and aesthetic appeal and has a rich historical legacy.
Historical Legacy:
Origins
Saddle stitching finds its roots in ancient civilizations. The Egyptians, for example, used a form of saddle stitching to bind papyrus scrolls.
By puncturing holes along the fold and threading cord or twine through them, they created secure bindings for their important texts.
Similarly, the Romans employed a similar technique for leather-bound documents, demonstrating the universality and adaptability of this method.
Medieval Manuscripts
During the medieval period, illuminated manuscripts were treasured works of art. Saddle stitching played a pivotal role in binding these masterpieces.
Skilled scribes meticulously wrote texts by hand, and equally talented binders used saddle stitching to assemble and secure the pages.
The craftsmanship in writing and binding processes resulted in some of history’s most exquisite and enduring literary works.
Leatherworking
In the realm of leatherworking, saddle stitching held immense importance. Craftsmen used this technique to create various goods, from intricately designed clothing to durable armor.
The technique’s strength and durability made it indispensable for producing items meant to withstand the test of time.
Even today, skilled leatherworkers use saddle stitching to create high-quality, handcrafted leather goods.
Bookbinding
As the popularity of printed materials grew, so did the demand for efficient and cost-effective binding methods. Saddle stitching was well-suited for binding booklets, pamphlets, and small publications.
Its straightforward process and reliable results made it a preferred choice, especially in producing magazines, catalogs, and other similar materials.
Industrial Revolution
The advent of the industrial revolution revolutionized many aspects of production, and saddle stitching was no exception.
Inventors and engineers developed mechanized saddle stitching machines, drastically increasing the speed and consistency of production.
This innovation paved the way for the mass production of books, magazines, and other printed materials, democratizing access to knowledge and literature.
Contemporary Usage
In today’s world, where technology advances, saddle stitching remains relevant.
While alternative binding methods have emerged, saddle stitching remains a favored choice for specific applications. It continues to be the go-to method for producing smaller publications, such as zines and art books.
Additionally, in the realm of leatherworking, artisans who prioritize craftsmanship and durability continue to employ saddle stitching to create bespoke leather goods.
How to Do a Saddle Stitch?
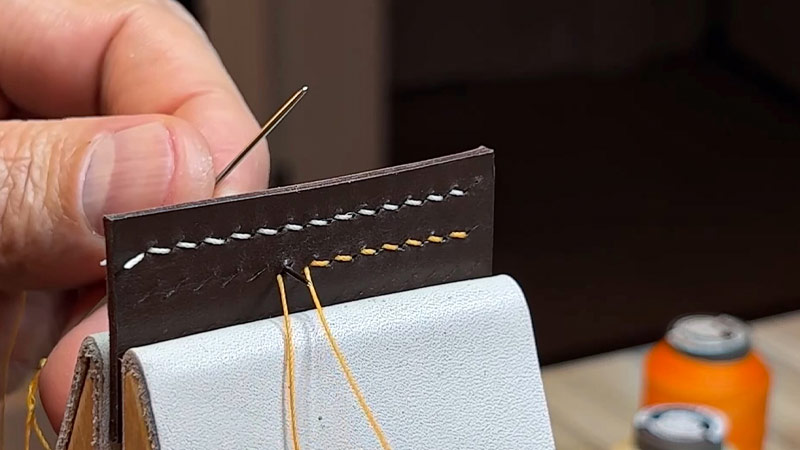

A saddle stitch is a simple and effective binding method for booklets, brochures, and other small publications.
It’s called “saddle stitch” because the pages are nestled together like they’re sitting in a saddle.
Here’s how you can do it:
Materials Needed:
- Sheets of paper
- Bone folder or spoon for creasing
- Needle
- Thread
- Scissors
- Pencil or awl for marking holes
Steps:
Prepare Your Materials
Begin by ensuring that your folded sheets of paper are arranged correctly to form the pages of your booklet. Take a moment to double-check that everything is in sequence.
If there’s any excess paper along the edges, carefully trim it away using a cutting mat and a utility knife or scissors.
Mark and Punch Holes
Spread out your folded sheets on a flat, stable surface. With a ruler, measure and mark points along the spine where you’ll make holes.
The number of holes can vary depending on your preference, but 3 or 4 evenly-spaced holes are common.
Using an awl or hole-punching tool, create holes at these marked points. Make sure the holes are aligned neatly along the spine.
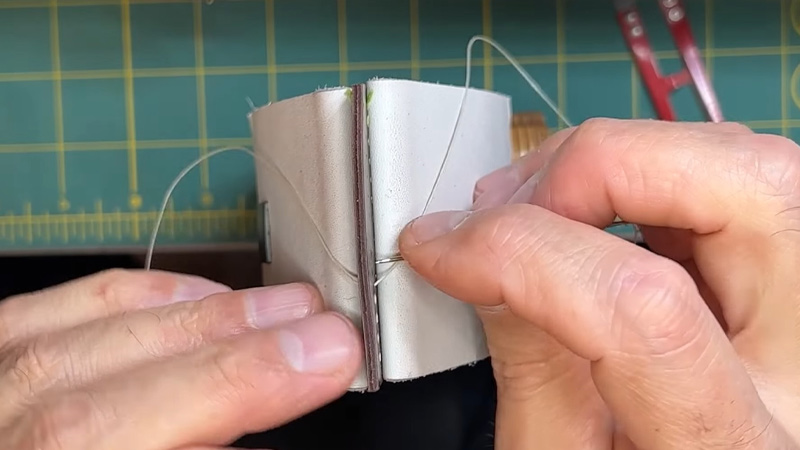
Thread the Needle
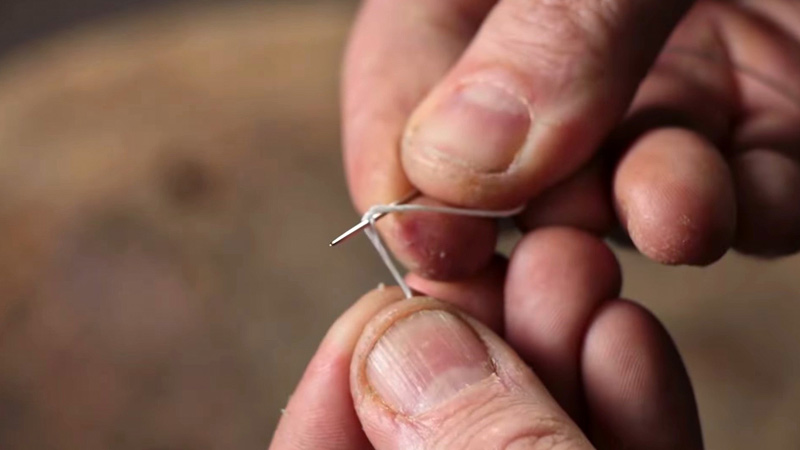

Thread a needle with a length of waxed linen thread. The thread should be about three times the height of your booklet.
Ensure that the end of the thread is securely knotted to prevent it from slipping out of the needle.
Start Stitching
Begin by inserting the threaded needle from the inside of the booklet (through the centerfold) to the outside through the bottom hole.
Leave a small tail of thread hanging inside the booklet to ensure it doesn’t pull through.
Continue Stitching
Proceed by reinserting the needle from the outside to the inside through the next hole up.
Then, please bring it back out through the hole above it. Continue this process until you’ve gone through all the holes, creating a straight line of stitches along the spine.
Tighten and Tie Knot
After each stitch, pull the thread tight to ensure that the pages are held together securely.
Once you’ve completed all the stitches, tie a knot with the two ends of the thread on the inside of the booklet. Make sure this knot is tight and secure.
Trim Excess Thread
Use scissors or a cutting tool to trim any excess thread inside the booklet carefully. This step helps give your booklet a clean and polished appearance.
Fold and Finish
Close the booklet, ensuring that the pages are aligned neatly. Use a bone folder or the side of your thumb to firmly crease the spine.
This action gives the booklet a professional finish and helps it lie flat.
Advantages of Saddle Stitch
Saddle stitching is a popular binding method used in the printing and publishing industry for creating booklets, brochures, magazines, and other printed materials.
It involves folding sheets of paper in half and stapling them along the fold line.
This method offers several advantages:
Cost-Effective
Saddle stitching is a highly cost-effective binding method, particularly well-suited for projects with limited budgets.
The materials required are minimal, consisting mainly of folded sheets of paper and staples. This simplicity reduces production costs, making it an economical choice for small to medium print runs.
Lay-Flat Capability
One of the distinctive advantages of saddle stitching is its ability to allow printed materials to lie flat when opened.
This characteristic is invaluable for items like cookbooks, catalogs, and instructional manuals, where readers benefit from a clear, unobstructed view of content across both pages.
Quick Turnaround
Saddle stitching is known for its efficiency, translating into shorter production times.
The straightforward process and minimal setup requirements mean that projects can be completed swiftly. This makes it an excellent choice for meeting tight deadlines or when rapid delivery of printed materials is crucial.
Suitable for Various Sizes
Another significant advantage of saddle stitching is its adaptability to different booklet sizes.
Whether producing small pocket-sized brochures or larger-format magazines, this binding method offers versatility in terms of the final dimensions of the printed piece.
Minimal Page Count Restrictions
Although there are limitations to the number of pages that can be saddle-stitched effectively, this method still accommodates many projects.
A combination of multiple saddle-stitched booklets can be used for longer documents, ensuring that content is organized and presented effectively.
Professional Appearance
Saddle-stitched publications exude a clean and professional appearance.
The staples are strategically placed within the fold, ensuring they are discreet and do not detract from the overall aesthetic.
This results in a polished final product that leaves a positive impression on readers.
Eco-Friendly
Saddle stitching is an environmentally conscious choice, generating minimal waste in the production process.
Unlike other binding methods involving adhesive or plastic elements, saddle stitching primarily relies on paper and metal staples.
This makes it a sustainable option for businesses and individuals seeking to minimize their environmental impact.
Easy to Handle
Saddle-stitched booklets are user-friendly and easy to handle. They are lightweight and compact, making them convenient for distribution and storage.
Whether for mailing, displaying at events, or providing to clients, saddle-stitched publications’ manageable size and weight simplify logistics and enhance overall usability.
Customization Options
Despite its simplicity, saddle stitching allows for various customization options.
Different paper types, weights, and finishes can create a unique and eye-catching final product.
Cover stocks and coatings can also be selected to enhance durability and visual appeal, ensuring the printed material aligns with specific branding or design preferences.
Difference Between a Saddle Stitch and a Lockstitch
Saddle stitch and lockstitch are two sewing techniques commonly used in various applications, including bookbinding and sewing machines.
Here are the key differences between the two:
Saddle Stitch
- Hand Sewing Technique: Saddle stitching is primarily a hand-sewing technique in bookbinding and leatherworking.
- Needle and Thread: Using a needle and a single continuous thread length. The needle is passed through the material, creating a series of interlocking loops.
- Durability: While it can be strong and durable, the strength of a saddle stitch largely depends on the quality of the stitching and the material being used.
- Visible Knots or Loops: In saddle stitching, you can typically see the knots or loops where the thread passes through the material. This can be an aesthetic choice.
- Aesthetics: Saddle stitching can be considered more traditional and is often chosen for its decorative and handcrafted look.
Lockstitch
- Machine Sewing Technique: Lockstitch is a sewing technique typically performed by a sewing machine.
- Two Threads: It uses two threads – one from the top (needle thread) and one from the bobbin (bottom thread). These threads interlock inside the material being sewn.
- Uniform Stitching: Lockstitching produces a more uniform and consistent result than hand-sewn saddle stitching.
- Strength and Durability: Lockstitching is strong and used in various applications, from clothing to upholstery.
- Cleaner Finish: Lockstitching often produces a cleaner and more polished finish than saddle stitching.
FAQS
What is saddle stitch in sewing?
Saddle stitch is a hand-sewing technique commonly used in bookbinding and leatherworking.
How is saddle stitch different from other sewing techniques?
Unlike machine stitching, which uses multiple threads and is done by a sewing machine, saddle stitch is a manual technique that relies on a single thread.
What are the advantages of using saddle stitch?
The saddle stitch provides a strong and durable seam, making it ideal for applications where longevity is important.
Where is saddle stitch commonly used?
Saddle stitch is widely employed in bookbinding to bind pages together and in leatherworking to join pieces of leather.
Is saddle stitching suitable for beginners?
Saddle stitching requires a certain level of skill and precision, as it is typically done by hand.
To Wrap Up
Saddle stitch stands as a testament to the enduring artistry of hand-sewn craftsmanship.
Its elegance lies in the simplicity of a single thread weaving through materials, creating a robust and distinctive bond.
Whether employed in bookbinding or leatherworking, this technique imparts a timeless quality to the finished product.
The visible loops and knots witness the meticulous attention and skill invested in each stitch.
As a testament to tradition, saddle stitch continues to be cherished for its durability and unique aesthetic appeal. It serves as a reminder that in a world of automation, there is an enduring beauty in the touch of the human hand.
Leave a Reply